Exploring an Example of Descriptive Statistics: Unveiling Data Insights
The Importance of Descriptive Statistics in Data Analysis
Descriptive statistics play a crucial role in summarizing and interpreting data, providing valuable insights into the characteristics and patterns present within a dataset. By using various statistical measures, researchers and analysts can effectively communicate the key features of their data, facilitating better decision-making and understanding of complex phenomena.
One common example of descriptive statistics is the calculation of measures such as mean, median, and mode. These central tendency measures help to identify the average value or most frequently occurring value in a dataset, providing a quick snapshot of the data’s distribution. For instance, in a survey of customer satisfaction ratings for a product, the mean rating can give an idea of the overall satisfaction level among customers.
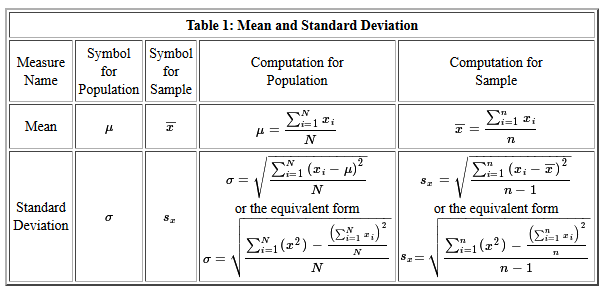
Another important aspect of descriptive statistics is dispersion measures, including range, variance, and standard deviation. These measures quantify the spread or variability of data points around the central value. For example, in analyzing sales data for a retail store, knowing the standard deviation can indicate how sales figures deviate from the average, helping to assess consistency or variability in performance.
Furthermore, graphical representations like histograms, box plots, and scatter plots are valuable tools for visually summarizing data distributions and relationships. These visualizations enhance understanding by providing intuitive representations of patterns and trends present in the data.
Descriptive statistics are not only limited to numerical data but can also be applied to categorical variables through frequency tables and bar charts. These methods help summarize categorical data by displaying counts or percentages within each category, enabling comparisons and insights into distribution patterns.
In conclusion, descriptive statistics serve as a foundation for exploring and interpreting data by offering concise summaries that aid in decision-making processes across various fields such as business analytics, social sciences, healthcare research, and more. By leveraging descriptive statistical techniques effectively, analysts can uncover meaningful insights from raw data and communicate findings in a clear and informative manner.
Mastering Descriptive Statistics: 7 Essential Tips for Analyzing Data
- Understand the measures of central tendency such as mean, median, and mode.
- Learn about measures of dispersion like range, variance, and standard deviation.
- Use histograms or bar charts to visualize the distribution of data.
- Calculate percentiles to understand the relative standing of a particular value in a dataset.
- Consider skewness and kurtosis to assess the symmetry and shape of the data distribution.
- Utilize scatter plots to examine relationships between two continuous variables.
- Interpret descriptive statistics in context to draw meaningful conclusions about the data.
Understand the measures of central tendency such as mean, median, and mode.
Understanding the measures of central tendency, including mean, median, and mode, is essential in descriptive statistics. These measures provide valuable insights into the typical or central values of a dataset, helping to summarize the data distribution in a meaningful way. The mean represents the average value of a set of numbers, while the median is the middle value when the data is arranged in ascending or descending order. On the other hand, the mode refers to the most frequently occurring value in the dataset. By grasping these central tendency measures, analysts can gain a comprehensive understanding of the data’s key characteristics and make informed interpretations based on these statistical summaries.
Learn about measures of dispersion like range, variance, and standard deviation.
Understanding measures of dispersion such as range, variance, and standard deviation is essential in descriptive statistics. These metrics provide valuable insights into the spread or variability of data points around the central tendency, offering a more comprehensive view of the dataset’s distribution. The range indicates the difference between the highest and lowest values, while variance and standard deviation quantify the average squared deviation from the mean, with standard deviation being particularly useful due to its interpretation in the same units as the original data. By learning about these measures of dispersion, analysts can better assess the consistency, variability, and overall patterns within their data, leading to more informed decision-making and insightful data analysis.
Use histograms or bar charts to visualize the distribution of data.
Histograms or bar charts are powerful tools in data analysis for visualizing the distribution of data. By displaying the frequency or proportion of data points within predefined intervals or categories, histograms and bar charts offer a clear and intuitive representation of the underlying patterns and trends present in the dataset. These graphical representations enable researchers and analysts to quickly identify outliers, assess the shape of the distribution, and gain insights into the central tendencies and variability of the data. Whether exploring numerical data in histograms or categorical data in bar charts, visualizing data distributions enhances understanding and facilitates effective decision-making based on descriptive statistics.
Calculate percentiles to understand the relative standing of a particular value in a dataset.
Calculating percentiles is a valuable technique in descriptive statistics that allows us to assess the relative standing of a specific value within a dataset. By determining the percentile rank of a data point, we can understand its position compared to other values in the distribution. For example, knowing that a particular test score falls at the 75th percentile indicates that 75% of the scores are below it, providing insight into its relative performance within the group. Percentiles help contextualize individual data points within the broader dataset, offering a deeper understanding of their significance and standing in relation to others.
Consider skewness and kurtosis to assess the symmetry and shape of the data distribution.
When analyzing data using descriptive statistics, it is essential to consider skewness and kurtosis as measures to assess the symmetry and shape of the data distribution. Skewness indicates the degree of asymmetry in the distribution, with positive values suggesting a longer tail on the right side and negative values indicating a longer tail on the left side. On the other hand, kurtosis measures the peakedness or flatness of a distribution, with higher kurtosis indicating sharper peaks and heavier tails. By examining skewness and kurtosis values, analysts can gain deeper insights into the underlying characteristics of the data distribution, helping them make more informed decisions and interpretations based on the shape of the data.
Utilize scatter plots to examine relationships between two continuous variables.
Utilizing scatter plots is a valuable technique in descriptive statistics to visually examine relationships between two continuous variables. By plotting data points on a graph where each point represents a pair of values from the two variables, analysts can easily identify patterns, trends, and correlations within the dataset. Scatter plots provide a clear visualization of how one variable may be affected or influenced by changes in another, helping to uncover potential associations or dependencies that may exist between the variables. This visual representation enhances understanding and facilitates deeper insights into the nature of the relationship, making it a powerful tool for data exploration and analysis.
Interpret descriptive statistics in context to draw meaningful conclusions about the data.
Interpreting descriptive statistics in context is essential for drawing meaningful conclusions about the data. By considering the specific characteristics of the dataset and understanding the context in which the data was collected, analysts can extract valuable insights and make informed decisions. For example, knowing that the average income in a certain region is $50,000 may seem significant on its own, but when interpreted in the context of cost of living, inflation rates, and other economic factors, it provides a more nuanced understanding of the region’s socioeconomic status. Contextual interpretation of descriptive statistics enables researchers to uncover underlying patterns, trends, and relationships within the data, ultimately leading to more accurate and actionable conclusions.



